Sustainability is the driving force for the protein transition, which continues to achieve traction globally. However to reach the long run, it have to be supported by financial advantages for the producer. Within the face of exterior components such because the unstable vitality market and legislative efforts to cut back greenhouse gases, producers could search to enhance the worth of different proteins by decreasing the price of producing them. However Kevin van Koerten, Challenge Supervisor Processing at NIZO, explains that there’s one other method: empowering sustainability within the meals transition by means of modern processing and sequential extraction and purification, to ship larger worth different proteins.
How do you improve the worth of a plant protein?
Any dialog round protein worth should begin with performance, as a result of meals product improvement is constructed round practical elements. This might embrace structured supplies delivering ‘chunk’, binders that hold merchandise collectively, or emulsifiers that hold drinks combined. Whereas there’s some innovation in mildly extracting less-refined proteins with extra basic fractions that may ship, for instance, mixed functionalities, this method would require a radical change in how merchandise are developed. Subsequently, with the present product improvement method, once you want to exchange an animal-origin ingredient with another, you should extract a protein ingredient with the capabilities you need.
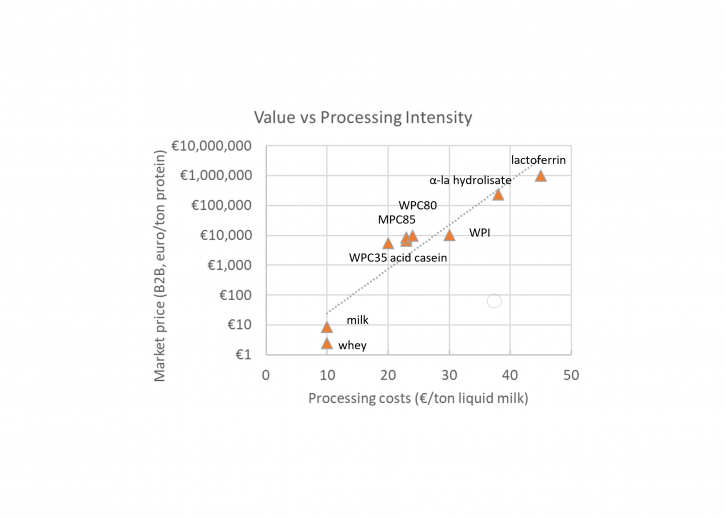
Each worth and price rise with protein performance. Nevertheless, the dairy trade exhibits us that this isn’t a linear relationship: extra practical proteins value extra to extract, however their market worth then will increase exponentially. Moreover, it’s doable to optimise the complete worth of a protein supply by means of sequential purification of proteins.
What’s sequential purification of proteins?
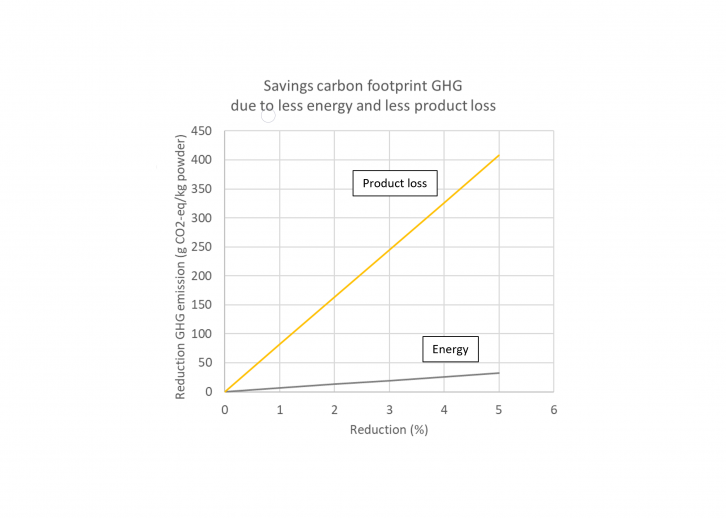
Sequential purification entails extracting a number of forms of proteins from the protein supply, utilizing completely different extraction methods. The dairy trade has perfected this method over the previous 50-70 years. It lets you maximise the worth extracted from the protein supply, and use extra of the supply materials, which reduces waste and product loss. Lowering product waste has been proven to result in larger reductions in greenhouse gases and vitality prices than efforts to chop vitality utilization.
Is it doable to attain the identical outcomes with plant proteins?
Plant protein producers are already taking the primary steps, extracting a number of proteins with completely different functionalities from a single supply. So whereas you used to have a single ‘potato protein’ or ‘pea protein’, now you’ll have an acid-soluble protein fraction and a neutral-soluble protein fraction. Nevertheless, there’s loads of exploratory work to be carried out, to determine all of the completely different proteins that may be extracted, after which to optimise the method design to get essentially the most worth. It’s a fancy problem.
What are the challenges of optimising processing design for plant proteins?
Firstly, all milk is basically the identical, and responds to processing in the identical manner. However each different protein supply and composition is completely different, and presents its personal challenges. On the opposite hand, there are some widespread challenges most plant proteins share, corresponding to larger viscosity, which negatively impacts processing effectivity by means of, for instance, elevated blockage of apparatus.
One other problem is that in protein extraction and processing, plant proteins can lose performance, flavour and solubility. Revolutionary gentle processing methods can present an answer to this, providing a substitute for acid precipitation, which can be cheaper and simpler to make use of, however which will increase product loss and reduces performance.
What gentle methods can be utilized? One necessary improvement has been in using polymer or ceramic membranes to filter the fabric stream. It’s been confirmed within the dairy trade, and is now transferring into plant protein extraction. Membrane filtration delivers larger yields and higher performance than acid precipitation, and is extra ecologically pleasant. By combining completely different membrane and processing circumstances at completely different levels, you may extract completely different proteins with completely different functionalities.
Are there hurdles to utilizing membranes?
Plant proteins can result in elevated fouling of membranes, on account of a wide range of mechanisms: the excessive viscosity already talked about, for instance. Methods corresponding to ultrasound or nano bubbles, or adapting the pretreatment, might be able to resolve this difficulty. Moreover, there’s loads of analysis and improvement going down on the membranes themselves, for instance adapting the polarity, which can cut back the flexibility of polyphenolics to connect and block the membrane pores. We want any such innovation to optimise the potential of the plant proteins.
How can producers ship that innovation?
Fortunately, we don’t have to begin utterly ‘from scratch’: each producers and meals analysis firms like NIZO have collected loads of information that may be useful. At NIZO, for instance, we’ve a really broad vary of information that can be utilized to assist choose the perfect place to begin, or the optimum subsequent step, together with exploring which plant proteins would possibly be capable to ship the required performance.
Producers, alternatively, have lots of in-depth information on their particular processes and merchandise. And with sensors now so available, they’ll accumulate much more, at each stage of processing. This information may present perception into particular alternatives for optimisation. Methods corresponding to modelling and synthetic intelligence (AI) are key to exploiting such information, to allow each a quicker design trajectory and a better success price for course of optimisations.
How can methods corresponding to modelling and AI give producers a ‘serving to hand’?
Modelling, for instance, might help ‘fill within the blanks’ of lacking information: consider utilizing high-throughput screening to outline optimum hydrolysis circumstances. AI can then take a look at your entire information panorama and discover patterns people won’t see. Nevertheless, AI outcomes are removed from good; you continue to want educated people to sift by means of the outcomes, to filter out the unrealistic AI-generated solutions and outcomes.
With all of the challenges, is it value it for manufactures to look past the ‘low-hanging fruit’?
The trade has solely touched the floor of what we will do with plant proteins. Can they be sustainable? Sure. However they’ll additionally make good enterprise and monetary sense for producers, particularly for those who can extract all of the potential worth. You want an understanding of each processing methods and protein sources. And you should take a holistic method, which seems to be on the course of from begin to end. It’s a serious problem for the trade, and we’re simply originally of the journey, however we imagine the payoff shall be greater than definitely worth the effort and investments.